NCL Home>
Application examples>
Data sets ||
Data files for some examples
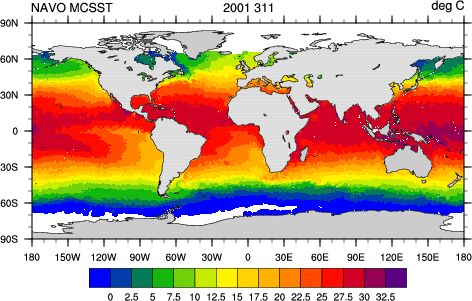
 mcsst_1.ncl: The NCL built-in
function fbindirread can be used to read NAVO
MCSST data. It's a simple process to expand this to float data and
apply the constants that transform the data into actual SST's.
mcsst_1.ncl: The NCL built-in
function fbindirread can be used to read NAVO
MCSST data. It's a simple process to expand this to float data and
apply the constants that transform the data into actual SST's.
 mcsst_2.ncl: Same script as example
1. Just demonstrates the non-interpolated data. I found that in areas
with sparse data (e.g. the Caribbean), the interpolated values were
greatly different from the observed values. If you plan to use this
data for feature identification, verify your results with the observed
values.
mcsst_2.ncl: Same script as example
1. Just demonstrates the non-interpolated data. I found that in areas
with sparse data (e.g. the Caribbean), the interpolated values were
greatly different from the observed values. If you plan to use this
data for feature identification, verify your results with the observed
values.
 mcsst_3.ncl: Demonstrates zooming in
on a subregion. We can turn off raster mode now, since the area is
smaller.
mcsst_3.ncl: Demonstrates zooming in
on a subregion. We can turn off raster mode now, since the area is
smaller.
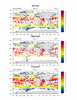 mcsst_4.ncl: Used a Fortran shared
object (composit.f) to create a
composite image of a day and night pass. Because of the grid, a
double loop of this size is extremely slow in an interpreted
computer language like NCL. (IDL and MatLab would have similar
issues). The external routine is simplistic, but significantly
increases speed. You will want to use WRAPIT to compile the
shared object.
mcsst_4.ncl: Used a Fortran shared
object (composit.f) to create a
composite image of a day and night pass. Because of the grid, a
double loop of this size is extremely slow in an interpreted
computer language like NCL. (IDL and MatLab would have similar
issues). The external routine is simplistic, but significantly
increases speed. You will want to use WRAPIT to compile the
shared object.
Example pages containing:
tips |
resources |
functions/procedures
NCL: NAVO MCSST

NAVO Multi-Channel Sea Surface Temperature (MCSST) data is in byte
format. See the examples below for information on how to use
NCL to read and plot this data.
 mcsst_1.ncl: The NCL built-in
function fbindirread can be used to read NAVO
MCSST data. It's a simple process to expand this to float data and
apply the constants that transform the data into actual SST's.
mcsst_1.ncl: The NCL built-in
function fbindirread can be used to read NAVO
MCSST data. It's a simple process to expand this to float data and
apply the constants that transform the data into actual SST's.
sst = new((/1024,2048/),"float")
sst = bytedata*xslope+yint: will convert the byte data to a float and
calculate the true SST values.
See script for how lat/lon coordinate variables are created.
 mcsst_2.ncl: Same script as example
1. Just demonstrates the non-interpolated data. I found that in areas
with sparse data (e.g. the Caribbean), the interpolated values were
greatly different from the observed values. If you plan to use this
data for feature identification, verify your results with the observed
values.
mcsst_2.ncl: Same script as example
1. Just demonstrates the non-interpolated data. I found that in areas
with sparse data (e.g. the Caribbean), the interpolated values were
greatly different from the observed values. If you plan to use this
data for feature identification, verify your results with the observed
values.
 mcsst_3.ncl: Demonstrates zooming in
on a subregion. We can turn off raster mode now, since the area is
smaller.
mcsst_3.ncl: Demonstrates zooming in
on a subregion. We can turn off raster mode now, since the area is
smaller.
For greater detail, we have changed to a higher resolution coastline by setting: mpDataBaseVersion = "MediumRes".
When you plot a sub region, you need to turn off the cyclic point which is automatically added to each plot. This is done by setting: gsnAddCyclic = False
To zoom in on a region, you need to set the following resources:
mpMinLonF
mpMinLatF
mpMaxLonF
mpMaxLatF
 mcsst_4.ncl: Used a Fortran shared
object (composit.f) to create a
composite image of a day and night pass. Because of the grid, a
double loop of this size is extremely slow in an interpreted
computer language like NCL. (IDL and MatLab would have similar
issues). The external routine is simplistic, but significantly
increases speed. You will want to use WRAPIT to compile the
shared object.
mcsst_4.ncl: Used a Fortran shared
object (composit.f) to create a
composite image of a day and night pass. Because of the grid, a
double loop of this size is extremely slow in an interpreted
computer language like NCL. (IDL and MatLab would have similar
issues). The external routine is simplistic, but significantly
increases speed. You will want to use WRAPIT to compile the
shared object.
WRAPIT composit.f