NCL Home>
Application examples>
Data Analysis ||
Data files for some examples
Example pages containing:
tips |
resources |
functions/procedures
NCL: Transects and Cross Sections
The calculation of a lat/lon transect involves the following steps:
- Determine the two lat/lon pairs that define the ends of the transect
- Calculate the great circle path between the two lat/lon pairs using
gc_latlon
- If your data is not rectilinear, then interpolate it a rectilinear grid
- Interpolate the input grid to the great circle using
linint2_points
A simple example of drawing only a straight line and
great circle path is availble. See the polyline
Example 14
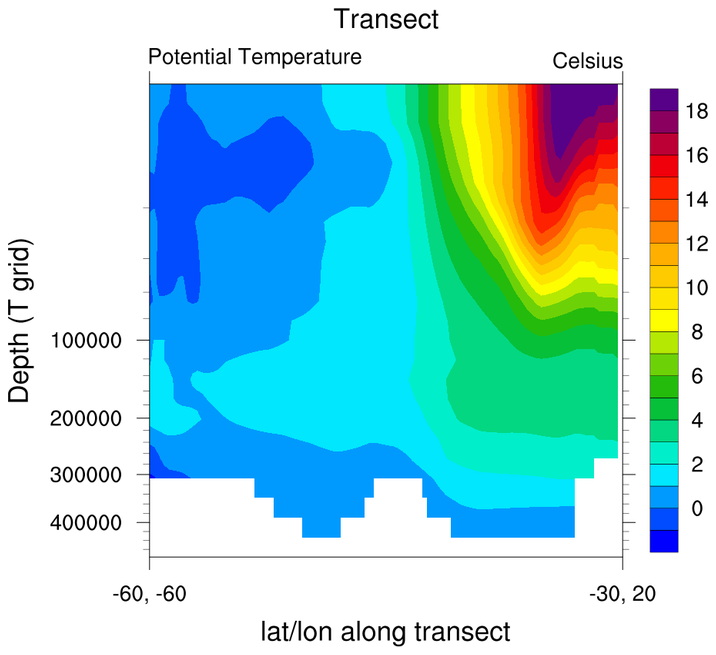
 trans_1.ncl
trans_1.ncl: Calculates and plots a
transect and also plots the transect location on a separate plot.
The data is on a rectilinear
grid, so no regridding is necessary before
calling linint2_points to interpolate values to an
arbitrary lat/lon line.
 asr_5.ncl
asr_5.ncl:
Draw a vertical cross section at an arbitary longitude position
(indicated by the blue line). This data is on
a
curvilinear grid,
which means each point is represented by a unique lat,lon pair.
Thus, when plotting the X axis, this example labels both lat
and lon values at each tickmark location.
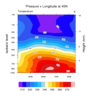
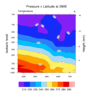
 narr_5.ncl
narr_5.ncl:
The NARR data is on a
curvilinear
grid. This script uses an ESMF generated weight file
(see
ESMF example 30) to first regrid
the NARR curvilinear grid to a rectilinear grid. Then three cross
sections are plotted: (a) pressure x longitude; (b) pressure x
latitude; and (c) pressure x user_specified_set_of_points.
For this example the user specified latitude/longitude locations lie
along a great circle path between two user specified locations
(see gc_latlon). They could be latitude/longitude
locations along a (say) cold front.
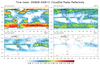
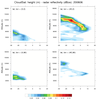
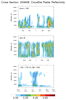 cloudsat_1.ncl
cloudsat_1.ncl
This example shows three kinds of cross sections of data
on a
rectilinear grid:
- Average "CloudSat Radar Reflectivity" over the period 200606-200612
at user specified levels.
- Radar reflectivity in the vertical at user specified (lat,lon) locations.
- User-specified cross sections. This uses
linint2_points_Wrap to
interpolate to a series of arbitrary
points. The gc_latlon function is used to generate
the points on a great circle path.