NCL Home>
Application examples>
Data Analysis ||
Data files for some examples
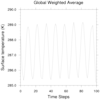 ave_1.ncl: Reads in a variable from a
netCDF file, calculates the global weighted average, and creates a
plot of the resulting time series.
ave_1.ncl: Reads in a variable from a
netCDF file, calculates the global weighted average, and creates a
plot of the resulting time series.
wgt_areaave is the NCL function that will calculate a weighted area average.
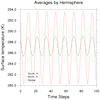 ave_2.ncl: Calculates a hemispheric
average, adds colored lines, and a plot legend.
ave_2.ncl: Calculates a hemispheric
average, adds colored lines, and a plot legend.
nh = wgt_areaave(ts(:,{0:90},:),gw({0:90}),1.0,0) Note the syntax using the curly brackets. This allows you to process a sub-set of the parent array using actual values in the latitude coordinate variable. Note also, that the gaussian weights must be partitioned over the same sub-region.
 ave_3.ncl: Plots a horizontal map
with the volume average as a center string.
ave_3.ncl: Plots a horizontal map
with the volume average as a center string.
wgt_volave_ccm calculates the weight volume average.
For model files, the z-weights are the delta-pressures, which can be calculated usingdpres_hybrid_ccm
Example pages containing: tips | resources | functions/procedures
NCL: Weighted Averages
 ave_1.ncl: Reads in a variable from a
netCDF file, calculates the global weighted average, and creates a
plot of the resulting time series.
ave_1.ncl: Reads in a variable from a
netCDF file, calculates the global weighted average, and creates a
plot of the resulting time series.
wgt_areaave is the NCL function that will calculate a weighted area average.
 ave_2.ncl: Calculates a hemispheric
average, adds colored lines, and a plot legend.
ave_2.ncl: Calculates a hemispheric
average, adds colored lines, and a plot legend.
nh = wgt_areaave(ts(:,{0:90},:),gw({0:90}),1.0,0) Note the syntax using the curly brackets. This allows you to process a sub-set of the parent array using actual values in the latitude coordinate variable. Note also, that the gaussian weights must be partitioned over the same sub-region.
 ave_3.ncl: Plots a horizontal map
with the volume average as a center string.
ave_3.ncl: Plots a horizontal map
with the volume average as a center string.
wgt_volave_ccm calculates the weight volume average.
For model files, the z-weights are the delta-pressures, which can be calculated using