NCL Home>
Application examples>
Data Analysis ||
Data files for some examples
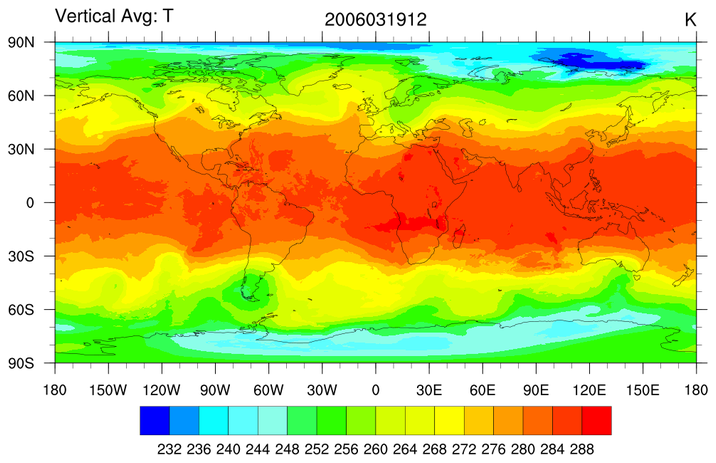
 cmplxgrb_1.ncl: Read complex coefficients
from an ECMWF created grib formatted file and reconstruct (synthesize) the
variable (800x1600) using shsgC. There are only four levels and the
surface pressure is not available but 'for fun' compute a vertical mean
temperature at each grid point. Compute layer thicknesses via dpres_plevel.
cmplxgrb_1.ncl: Read complex coefficients
from an ECMWF created grib formatted file and reconstruct (synthesize) the
variable (800x1600) using shsgC. There are only four levels and the
surface pressure is not available but 'for fun' compute a vertical mean
temperature at each grid point. Compute layer thicknesses via dpres_plevel.
 cmplxgrb_2.ncl: Read complex coefficients
from an ECMWF created grib formatted file. The full grid is 160x320 and a full
complex coefficient array would be 160x160. However, this is a T106 grid and
ECMWF only put out 107 coefficients (a constant plus 106 coefficients).
Reconstruct (synthesize) the variable (160x320) using shsgc.
The underlying spherical harmonic code requires a full size coefficient grid.
The approach is to preallocate space for a full coefficient array but only
fill the 1st 107 (0:106) values. All the rest are set to zero.
cmplxgrb_2.ncl: Read complex coefficients
from an ECMWF created grib formatted file. The full grid is 160x320 and a full
complex coefficient array would be 160x160. However, this is a T106 grid and
ECMWF only put out 107 coefficients (a constant plus 106 coefficients).
Reconstruct (synthesize) the variable (160x320) using shsgc.
The underlying spherical harmonic code requires a full size coefficient grid.
The approach is to preallocate space for a full coefficient array but only
fill the 1st 107 (0:106) values. All the rest are set to zero.
Example pages containing: tips | resources | functions/procedures
NCL Graphics: Complex Coefficients [GRIB]

Synthesize (reconstruct) a variable from spherical harmonic complex coefficients

 cmplxgrb_1.ncl: Read complex coefficients
from an ECMWF created grib formatted file and reconstruct (synthesize) the
variable (800x1600) using shsgC. There are only four levels and the
surface pressure is not available but 'for fun' compute a vertical mean
temperature at each grid point. Compute layer thicknesses via dpres_plevel.
cmplxgrb_1.ncl: Read complex coefficients
from an ECMWF created grib formatted file and reconstruct (synthesize) the
variable (800x1600) using shsgC. There are only four levels and the
surface pressure is not available but 'for fun' compute a vertical mean
temperature at each grid point. Compute layer thicknesses via dpres_plevel.
Examine the Grib file via:
ncl_filedump -itime ana_yest.800x800_complex.grb
[snip]
dimensions:
initial_time0_hours = 1
lv_ISBL1 = 4
real_imaginary = 2 ; coefficient array
g50_lat_3 = 800
g50_lon_4 = 800
g4_lat_5 = 800 ; target grid
g4_lon_6 = 1600
[snip]
float T_GDS50_ISBL(initial_time0_hours,lv_ISBL1, real_imaginary, g50_lat_3, g50_lon_4)
 cmplxgrb_2.ncl: Read complex coefficients
from an ECMWF created grib formatted file. The full grid is 160x320 and a full
complex coefficient array would be 160x160. However, this is a T106 grid and
ECMWF only put out 107 coefficients (a constant plus 106 coefficients).
Reconstruct (synthesize) the variable (160x320) using shsgc.
The underlying spherical harmonic code requires a full size coefficient grid.
The approach is to preallocate space for a full coefficient array but only
fill the 1st 107 (0:106) values. All the rest are set to zero.
cmplxgrb_2.ncl: Read complex coefficients
from an ECMWF created grib formatted file. The full grid is 160x320 and a full
complex coefficient array would be 160x160. However, this is a T106 grid and
ECMWF only put out 107 coefficients (a constant plus 106 coefficients).
Reconstruct (synthesize) the variable (160x320) using shsgc.
The underlying spherical harmonic code requires a full size coefficient grid.
The approach is to preallocate space for a full coefficient array but only
fill the 1st 107 (0:106) values. All the rest are set to zero.
Examine the Grib file via:
ncl_filedump Y42677.cc.grb
[snip]
dimensions:
initial_time0_hours = 44
lv_HYBL1 = 31
real_imaginary = 2
g50_lat_5 = 107 ; coefficient array
g50_lon_6 = 107
[snip]
float D_GDS50_HYBL(initial_time0_hours, lv_HYBL1, real_imaginary, g50_lat_5, g50_lon_6)
center : European Center for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (RSMC)
long_name : Divergence
units : s**-1
[snip]
To compute the divergent winds and velocity potential see
here.