NCL Home>
Application examples>
Plot techniques ||
Data files for some examples
Example pages containing:
tips |
resources |
functions/procedures
NCL Graphics: Color Maps
This suite of examples shows how to change, create, draw, reverse, and
otherwise manipulate colors and color maps (also known as "color
tables").
NCL has a built-in list of
available color
tables and a suite
of 650 named
colors you can use.
Note: in NCL V6.1.0, a new
color model was introduced, which replaces the concept of associating
color maps with a workstation. For backwards compatibility, the old
color model is still supported. Many of the examples here are
for the workstation color map, but can still be very useful for
both color models.
Here are some functions and procedures that are useful in
working with color maps and colors in general:
- draw_color_palette - draws the given colors or
color map as a series of filled boxes.
- get_color_rgba - chooses an RGB triplet or RGBA
quadruplet for a scalar value, given a color map and a range of
values.
- namedcolor2rgb /
namedcolor2rgba
- returns the RGB triplets or RGBA quadruplets of the given list of
named colors.
- read_colormap_file - reads an NCL system colormap
file or a user-defined colormap.
- span_color_rgba - given the
number of desired color values, return an array of RGB triplets or
RGBA quadruplets that nicely span the given color map.
- span_named_colors - returns an
RGB array that is a span between given list of named colors.
Here are some older functions that are useful when working
with the color map associated with the workstation:
CMYK color
If you need to use CMYK color, then this is only supported with the
old style color model (pre NCL V6.1.0), and hence you must use "oldps"
or "oldpdf" as the output format. You can set this via a workstation
resource, before you
call gsn_open_wks:
type = "oldps" ; cannot use "ps" or "pdf"
type@wkColorModel = "cmyk"
wks = gsn_open_wks(type,"example")
Note: a user reported a noticeable degradation in the color quality
when using the old postscript and pdf drivers along with the CMYK
option. He said he's been able to submit RGB figures to various
journals for the last few years, and never had a problem. If you have
to send in CMYK graphics, then submit the figures as RGB (which is the
default in NCL), and then use an external package like Illustrator to
convert them to CMYK.
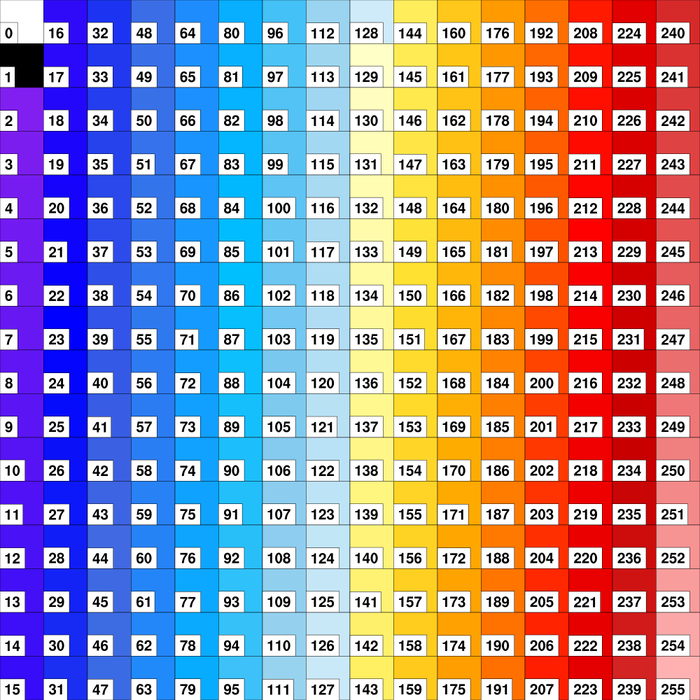
 colormap_1.ncl
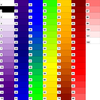
colormap_1.ncl: Demonstrates
drawing the current color map associated with the workstation
using
gsn_draw_colormap.
Note: if you are setting a color map in your .hluresfile, then your
output from this script may be different.
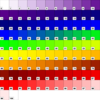

 colormap_2a.ncl
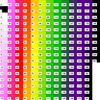
colormap_2a.ncl: This example
draws the same color maps as the previous example, but it uses
the
draw_color_palette procedure added in NCL
V6.3.0. This procedure doesn't require that you first
call
gsn_define_colormap to
set the color map.
Note that the color tables are drawn slightly differently than they
are with gsn_define_colormap. For
one, they are drawn left-to-right, top-to-bottom, rather than
top-to-bottom, left-to-right.
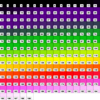
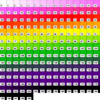 colormap_3a.ncl
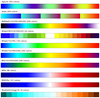
colormap_3a.ncl: This example is
similar to the previous example, except it shows how to reverse the
workstation color map using
read_colormap_file to
first read the color map, and then the array syntax "::-1" to reverse
it. It draws the color map using
the
draw_color_palette procedure added in NCL
V6.3.0.

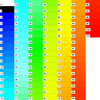
 colormap_4.ncl
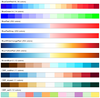
colormap_4.ncl: Demonstrates
merging two colormaps on the workstation
using
gsn_merge_colormaps. You can only do this
with two colormaps whose sum total is fewer than 256 colors.
The background/foreground colors are retained from the
first colormap only.
Note: merging color maps is not really necessary under the new color
model. See
example newcolor_13.ncl
on the RGBA examples page for a way to use multiple color maps on a
single page.
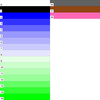 colormap_5.ncl
colormap_5.ncl: Demonstrates
adding colors to an existing colormap, using
NhlNewColor. This is only necessary for NCL
versions 6.0.0 or earlier, if you need to use one or
more
named colors
and they are not in your current color map. In version 6.1.0
and later, named colors do not need to be added.
In order to add named colors to a colormap, you need to get their
corresponding RGB triplet from the $NCARG_ROOT/lib/ncarg/database/rgb.txt
file. This will be in values from 0 to 255, so you first need to
divide the values by 255 to get an RGB triplet.
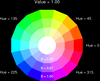
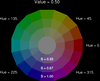
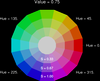 colormap_6.ncl
colormap_6.ncl: Uses
hsvrgb to draw some illustrative
HSV color wheels.
See the next example for how to create a colormap using this function.
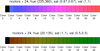 colormap_7.ncl
colormap_7.ncl: Uses values
from the above HSV color wheels to generate colormaps than span
from one color to another.
The colormap is drawn using gsn_labelbar_ndc.
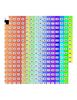

 colormap_8.ncl
colormap_8.ncl: Uses
span_named_colors
to generate a color table that spans between given
named colors.
You can optionally set the attributes "NumColorsInRange"
or "NumColorsInTable" to indicate the maximum number of
colors allowed in the table, or the number of colors in each
range between named colors.
 colormap_9.ncl
colormap_9.ncl: Uses the
span_named_colors function
to create a color map that reverses itself at the midpoint.
The colors passed to the function are
(/"red","green","blue","purple","blue","green","red"/), with
20 colors between each range.