NCL Home>
Application examples>
Plot techniques ||
Data files for some examples
Example pages containing:
tips |
resources |
functions/procedures
NCL Graphics: Color Fill
NCL
V6.1.0 introduced a new
color model, which replaces the concept of associating color maps with
a workstation. For backwards compatibility, the old color model is
still supported.
For more information about this color model, see
the RGBA color examples page.
Note: in the descriptions below, the terms "color table" and "color
map" are used interchangeably.
To set color fill for a contour, vector, or streamline plot, you can
use the following "Palette" resources:
The "Palette" resources can be set using:
To reverse or subset a predefined color map, use the
function read_colormap_file to read the file in as
an RGBA array (n x 4). You can then subset or reverse
it using normal NCL array subscripting:
cmap = read_colormap_file("BlGrYeOrReVi200")
res@cnFillPalette = cmap(::-1,:) ; reverse color map
res@cnFillPalette = cmap(10:100,:) ; subset color map
Other useful links:
For NCL versions
6.0.0 or
earlier, you have to use the workstation color map to set color for
contours, vectors, or streamlines. The primary routines and resources
for the old color model include:
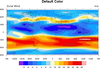 color_1.ncl
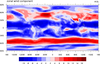
color_1.ncl: Demonstrates turning on
color with the default color map.
cnFillOn = True turns on
color fill for a contour plot
A Python version of this projection is available here.
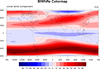
 color_2.ncl
color_2.ncl /
color_2_old.ncl:
Example of using a built in colormap.There are numerous
color tables to
choose from.
A new resource was introduced in V6.1.0 allowing you to specify a
color palette to use with your contours (independent of the
workstation color map):
cnFillPalette.
The cnSpanFillPalette
allows you to turn on/off the automatic span of the colors.
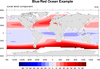
For best results when using the blue/red color spectrum, manually set
the contour levels so that the change centers on zero:
cnLevelSelectionMode = "ManualLevels"
cnMinLevelValF
cnMaxLevelValF
cnLevelSpacingF
The color_2_old.ncl script
demonstrates the old way (pre NCL V6.1.0) of assigning a color map
for color contours.
- gsn_define_colormap is used to
set a colormap for the given workstation.
- NhlNewColor(wks,0.8,0.8,0.8) adds gray
to the color map, which had to be done in NCL V6.0.0 and older.
- Setting gsnSpreadColors=True forces
the color map to be be spanned when creating a filled contour or
vector plot.
 color_3.ncl
color_3.ncl:
Demonstrates how to select just a few colors out of a large
colormap and make one of those colors transparent.
cnFillColors is the resource used
to select what colors out of a colormap you want to represent each
contour in the plot.
The -1 indicates that the color is transparent. This is not a true
color per say but rather the absence of color. As such, whatever color
the background is will be seen.
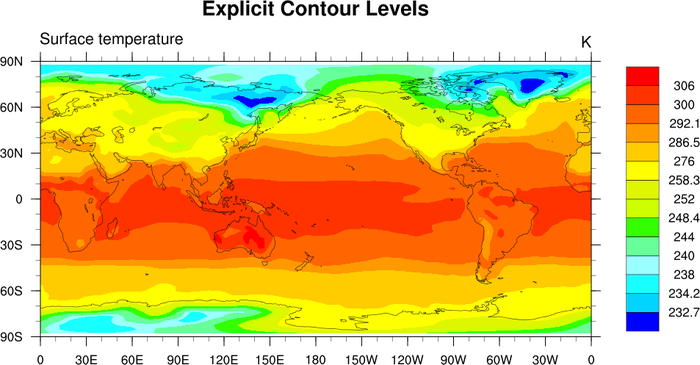
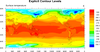 color_6.ncl
color_6.ncl: Creates a color plot
with uneven color intervals.
cnLinesOn = False, turns off
contour lines.
cnLevelSelectionMode="ExplicitLevels",
and cnLevels =
(/232.7,234.2,238,240,244,248.4,252,258.3,276,286.5, 292.1,300,306/)
manually sets the uneven contour levels.
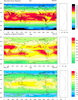 color_7.ncl
color_7.ncl: Another example of
choosing from a set of predefined color maps. Zonal average
automatically calculated and plotted. The label bar is moved from the
default horizontal to vertical.
gsn_define_colormap(wks,"uniform"),
Selects the "uniform" predefined color map. There are numerous
color
tables to choose from.
lbOrientation = "Vertical", Creates
a vertical label bar.
gsnZonalMean = True, Automatically
calculates and draws the zonal mean of the field. gsnZonalMeanXMaxF and gsnZonalMeanXMinF allow the user to change the
axis of the zonal average plot.

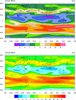 color_9.ncl
color_9.ncl /
color_9_new.ncl: Merges two
colormaps using
gsn_merge_colormaps,
so that multiple colormaps can be used on the same workstation.
Note that in V6.1.0, you do not need to merge colormaps in this
way. If you are drawing color contours, vectors, or streamlines, you
can associate a colormap with a plot using one of these new resources:
See the color_9_new.ncl script
for an example of
using cnFillPalette.
 color_10.ncl
color_10.ncl: I randomly chose
colors from the master list of
named
colors, and placed them in my own RGB file (
test_rgb.txt) to create a personalized
colormap.
RGBtoCmap is the function that
will take a text file of RGB triplets and convert them into an NCL
colormap. You can then use gsn_draw_colormap to preview what your
colormap looks like. This is an easy way to develop your own
colormaps.
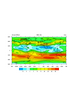 color_11.ncl
color_11.ncl: This exmaple shows
how to use CMYK color in your graphics. CMYK color is only recognized
using the old style color model (pre NCL V6.1.0), and hence you must
use "oldps" or "oldpdf" as the output format. You can set this via a
workstation resource, before you
call
gsn_open_wks:
type = "oldps"
type@wkColorModel = "cmyk"
wks = gsn_open_wks(type,"color")
Note: a user reported a noticeable degradation in the color quality
when using the old postscript and pdf drivers along with the CMYK
option. He said he's been able to submit RGB figures to various
journals for the last few years, and never had a problem. If you have
to send in CMYK graphics, then submit the figures as RGB (which is the
default in NCL), and then use an external package like Illustrator to
convert them to CMYK.
Second note: this example shows how to subselect a color map using the
"old style" resource gsnSpreadColors.
gsnSpreadColorStart allows you to choose
which color to start your color table at while gsnSpreadColorEnd allows you to choose which
color to end your color table.
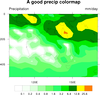 color_12.ncl
color_12.ncl: Demonstrates choosing
a colormap based upon the specification of an array of RGB triplets.
The array must be a float array, and must be normalized by dividing by
255.
This particular color map is specifically used for precipitation plots.
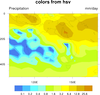 color_13.ncl
color_13.ncl: Demonstrates
how to convert an array of colors in HSV format to RGB format.
hsvrgb is the function that does
the conversion. See the script for usage. hsvrgb,
available in version 4.3.2 or later,
replaces the obsolete function hsv2rgb.
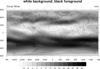
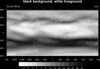 color_14.ncl
color_14.ncl: Demonstrates the use
of a grayscale color table (
gsltod).
The second frame shows how to change the background and foreground colors
to black and white.
Note that in order to change the foreground and background colors, you
must do this using workstation
resources: wkForegroundColor
and wkBackgroundColor.
setvalues wks
"wkForegroundColor" : (/1.,1.,1./) ; white
"wkBackgroundColor" : (/0.,0.,0./) ; black
end setvalues
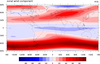 color_15.ncl
color_15.ncl: Uses
symMinMaxPlt to automatically calculate
symmetric min/max/int values for use with a symmetric colormap. This
is useful when running a script that plots multiple variables of
varying magnitudes.
 color_17.ncl
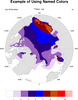
color_17.ncl: Draws the given list
of named colors using
gsn_draw_named_colors. This procedure
internally sets the colormap to the given list of named colors,
and then sets the color map back to the original color map before
exiting. It is mostly useful for debugging purposes.
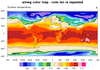
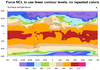
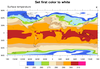 color_19.ncl
color_19.ncl: Shows how to change a
color in an existing color map. In this case,
the
amwg color
map is read in using
read_colormap_file, and the
first color is changed to white.
The amwg color map is relatively small (16 colors). Note that in the first
frame NCL chose 18 contour levels, and hence needs 17
colors to represent them. What happens in this case is that NCL will
start repeating some of the colors; in this case, the tan color
between levels 270 and 280.
To force NCL to choose fewer contour levels, you can
set cnMaxLevelCount to
ncolors-1, where ncolors is the number of colors
in your color table (not counting the background and foreground colors).