NCL Home>
Application examples>
Data sets ||
Data files for some examples
Example pages containing:
tips |
resources |
functions/procedures
NCL Graphics: Topographic maps
This page describes various ways to create topographic maps,
either by reading them from a binary or NetCDF file, or by
importing an existing JPEG image and recreating it.
You can find many free topographic maps (as datasets or images) on the
web, including a good site from NOAA:
http://www.ngdc.noaa.gov/mgg/topo/topo.html
There are some high-resolution images available via
Nasa's Blue Marble imagery and the 3rd party True Marble:
http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/Features/BlueMarble/?src=ve
http://www.unearthedoutdoors.net/global_data/true_marble/download
Importing JPEG images
Importing JPEG images into NCL requires converting the JPEG image to a
NetCDF file. We use a free tool called "gdal_translate", which is part
of the GDAL - Geospatial Data
Abstraction software package.
You can download
precompiled
binaries for Linux and Mac, or you can download
the source
code and build it yourself.
Building from source requires that you build GDAL with NetCDF support:
./configure --prefix=/path/for/install --with-netcdf=/path/to/netcdf
make all install
/path/for/install and
/path/to/netcdf are just
placeholders. You need to replace them with the appropriate paths.
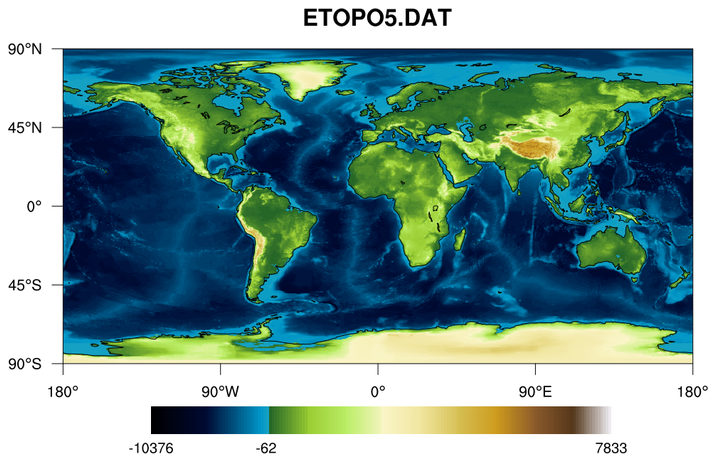
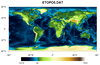
 topo_1.ncl
topo_1.ncl
This script draws a (now deprecated) 5' topographic map using binary data
downloaded from
http://www.ngdc.noaa.gov/mgg/global/relief/ETOPO5/TOPO/ETOPO5/
This binary file doesn't contain any latitude/longitude values, so
these arrays have to be generated in the script. The data comes with
a good
description of how to read it and create the lat/lon arrays.
The default NCL color map is used just to quickly show what the data looks like.
 topo_2.ncl
topo_2.ncl
This script uses the same data as the previous example, except
it uses a custom color map. The labelbar is labeled using min/max
labels, and a middle level to indicate where the color map was
split between ocean and land values.
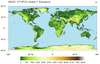 topo_3.ncl
topo_3.ncl
This script draws a (now deprecated) 2' topographic map using NetCDF data
downloaded from
http://www.ngdc.noaa.gov/mgg/fliers/01mgg04.html
The cnFillMode resource is set to "MeshFill" for
faster plotting. The default "AreaFill" is too slow.
The data are of type "short" with scale_factor and add_offset
attributes; the short2flt
function is used to unpack the values into a float type.
All elevation values less than -100 are set to missing so there are
effectively no contours over the ocean. The ocean is filled in with a
light blue.
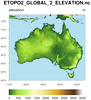 topo_4.ncl
topo_4.ncl
This script draws a topographic map from the same 2' data as the previous
example, except it zooms in on Australia and New Zealand.
"RasterFill" is used in place of "MeshFill" for comparison.
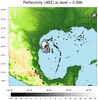 topo_7.ncl
topo_7.ncl
This example is similar to the WRF "newcolor_10.ncl" example on
the
new color capabilities page,
which shows how to plot "dbz" from a WRF output file on a terrain
map. Instead of using the "HGT" variable on the WRF output file to
plot terrain, it uses the 2' topo map from examples 3 and 4 above.
This gives you a better resolution for terrain, if you need it.
A different colormap is used for dbz, just to show how you can do
this. If you set ANIMATE to True, then the script will loop across
all levels.
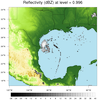 topo_raster_7.ncl
topo_raster_7.ncl
This example is almost identical to
topo_7.ncl
above except the reflectivity values are drawn as raster filled
contours instead of smooth contours. The point of this example is to
illustrate a quirk of using raster fill with transparency. In order
to get transparency with raster fill and RGBA values,
it's not enough to simply set the alpha value to 0.0. You must
also set the color to black as well:
; cmap_r(0,3) = 0.0 ; This won't work
cmap_r(0,:) = 0.0 ; This will work.
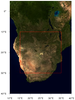 topo_9.ncl
topo_9.ncl
This script is based on the "newcolor_11.ncl" script
on the
New color capabilities
page. It shows how to use NCL to recreate an existing JPEG that contains a topographic map. By doing this, you can then change the map projection,
zoom in on it, and/or overlay primitives, as we did here with a red box.
The open source tool gdal_translate was
used to convert the jpeg file to a NetCDF file:
gdal_translate -ot Int16 -of netCDF EarthMap_2500x1250.jpg EarthMap_2500x1250.nc
This example only works for "x11" or "png" output, and not with
"ps" and "pdf" output.
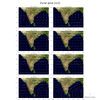
 panel_31.ncl
panel_31.ncl: This example shows
how to panel vector plots overlaid on topographic maps, and then
draw only one vector reference annotation box.
The vector reference annotation box is turned off for all plots except
the lower rightmost one, by setting
res@vcRefAnnoOn = False for all but
that one plot. The box is moved to the outside right of that plot by
setting res@vcRefAnnoParallelPosF.
The topographic map is created by reading in a JPEG image. See example
newcolor_11.ncl on the RGBA page.
This image can be slow to create, so set TOPO_MAP to False in the
script if you just want to generate a generic NCL map object (see
second thumbnail).