NCL Home>
Application examples>
Plot techniques ||
Data files for some examples
Example pages containing:
tips |
resources |
functions/procedures
NCL Graphics: Overlay Plots
Overlay plots are different plots (like vectors and contours) that are drawn
on top of each other, and possibly on top of a map.
There are many different ways that one can create overlay plots:
- Use the overlay procedure (this is the best method)
- Use the gsn_csm_contour_map_overlay plotting function (this method is not usually recommended)
- Manually overlay plots by drawing each plot and not advancing the frame
- Use NhlAddData to add a line, a legend, or other graphical object to an existing plot.
- If plotting WRF data, you can alternatively use the wrf_overlays or wrf_map_overlays plotting functions
There are numerous examples of overlay plots available across many different NCL web pages. A number of them can be
found on the Contours overlaid on contours Application page.
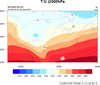 overlay_1.ncl
overlay_1.ncl:
Create individual plots with
gsn_csm_contour_map and
gsn_csm_contour, and use
overlay to combine them.
As we only wish that the overlaid plot be drawn, gsnDraw and gsnFrame are both set
to False in the two resource lists. After overlay is called, draw is called
to draw plot, which has had plot_ov overlaid on it. Finally, the frame is advanced, in essence completing the page.
Note that you are not allowed to use any gsn_csm_*_map plotting functions to create the 2nd input in
overlay, as an error message will result.
A Python version of this projection is available
here.
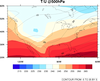 overlay_3.ncl
overlay_3.ncl:
Similar to examples 1 and 2, except here plot2 is manually drawn on plot by not advancing the frame upon the creation of plot.
Note that when manually overlaying, one strives to create each plot the exact same size in the exact same location on the page.
In this example, that was trivial. In some cases, the vpXF, vpYF, vpWidthF, and
vpHeightF resources, various titles and font heights all need to be set the same for both plots.
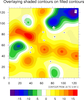 overlay_5.ncl
overlay_5.ncl:
Documents how to use
gsn_contour_shade to create an overlay plot that is then overlaid on the base plot
by using
overlay.
This is one way to overlay a pattern filled contour field on top
of a different color filled contour field. Another way can be found on
example 14 on the Contour Effects applications page.
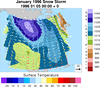 overlay_6.ncl
overlay_6.ncl:
Demonstrates how to overlay a color filled contour field,
streamlines, and color filled vectors all on one plot.
Two label bars are created, one for the color filled contour
field, and one for the color filled vector field. Individually 4
plots are created: A plot showing just a map, a color filled
contour field plot, a streamline plot, and a color filled vector
plot. overlay is then used to overlay the
contour, streamline and vector plot on the map plot.
The resources cnFillPalette
and vcLevelPalette are used
to indivudally assign color maps for the color contours and vectors.
A Python version of this projection is available here.
 overlay_7.ncl
overlay_7.ncl:
Documents how to overlay xy plots whose timeseries are of different sizes. As
gsn_csm_xy expects each input
timeseries to be the same size, this is one method that can be used to add timeseries of different lengths to a single plot.
gsn_add_annotation is used to add a legend to the overlaid plot, which allows the legend to be resized
if the plot itself is resized.
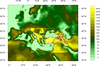 conOncon_9.ncl
conOncon_9.ncl: This image
describes land use in different resolutions for each domain. This
script was originally written in
PyNGL by Ufuk Utku Turuncoglu of
the Istanbul Technical University in relation to a Turkey Climate
Change Scenarios project.
The overlay
procedure is used to do the multiple contour overlays. These contours
are over a map, so the first contour (coarse) plot is created with
gsn_csm_contour_map, and the
other two contour plots are created using
gsn_csm_contour.
Polylines are drawn on top of the map to show the three domains.
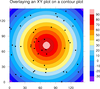 overlay_8.ncl
overlay_8.ncl:
Shows how to overlay a scatter plot on a contour plot. The key is
that the axes of both plots must be in the same data space.
The next example shows how to overlay two plots that are not
in the same data space.
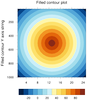
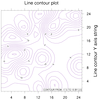
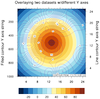
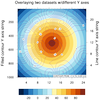 overlay_9.ncl
overlay_9.ncl /
overlay_9a.ncl:
Shows two different ways to overlay a line contour plot on a filled
contour plot when they have two different axes. The "overlay_9.ncl"
script uses
gsn_add_annotation to
add the line contour plot as an annotation of the filled contour plot.
The "overlay_9a.ncl" script uses
overlay procedure,
along with setting the
special
tfDoNDCOverlay resource to
True.
Note that the left axis corresponds with the filled contour plot,
and the right Y axes with the line contour plot.
Since the axes are not in the same data space, this example only works
if the Y ranges of the two plots line up exactly.
When you use overlay, the tickmarks and labels
get removed from the overlay plot. The "overlay_9a.ncl" example
adds them to the base plot on the Y right axis.
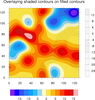 overlay_10.ncl
overlay_10.ncl:
Shows how to overlay a shaded contour plot on a filled contour plot
and get labelbars for both plots by drawing one vertically and
one horizontally.
 xy_32.ncl
xy_32.ncl: This example shows how to
draw a 8-curve XY plot with 4 legends stacked side-by-side.
In order to do this, it is necessary to create 4 XY plots, each with
two curves and two items in its legend. The legend for each plot is
moved to the right or left slightly so they don't overlap. The plots
are then all "connected" into one plot using
the overlay procedure.
 wrf_gsn_5.ncl
wrf_gsn_5.ncl
This example shows how to overlay line contours, vectors, and filled
contours on a map. The data and map projection are all read off a WRF
output file.
 wrf_nogsn_5.ncl
wrf_nogsn_5.ncl
This example is similar to the previous one, except it shows
how to use WRF plotting functions instead of gsn_csm plotting
functions.
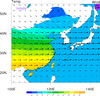 overlay_11.ncl
overlay_11.ncl:
This example shows how to overlay vectors on top of a filled contour plot,
where the contours are masked by a geographical area and the vectors
are not. The masking is accomplished by setting:
mpres@mpDataBaseVersion = "MediumRes"
mpres@mpMaskAreaSpecifiers = (/"China:states","Taiwan"/)
The mask area specifier names are part of the
predefined group
names available in the "MediumRes" map database.
This script was written by Yang Zhao (CAMS) (Chinese Academy of
Meteorological Sciences).
There are two versions of this projection available in Python. Version (a) is found here and version (b) is found here.
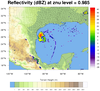
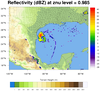 overlay_12.ncl
overlay_12.ncl:
This example shows how you can create two color contour plots, each
with their own color map, and then use the
overlay
procedure to overlay them into a single image.
The cnFillPalette
resource is used to set the color map for both plots. The
color map for the reflectivity contours is first
read in using read_colormap_file, so
that the first color can be set to transparent.
Transparency is used in both plots to subdue the colors in the terrain
map, and to make one of the colors in the reflectivity plot completely
transparent.
Important note: In NCL V6.3.0 and earlier the labelbar does not
reflect the same opacities as the filled contours; this bug was fixed
in NCL V6.4.0. A new resource
called lbOverrideFillOpacity was
introduced in NCL V6.4.0 which allows you to keep the labelbar colors
fully opaque independent of the opacity of the filled contours.
The first frame shows the partially opaque labelbar, and the
second frame shows a fully opaque labelbar created
by setting lbOverrideFillOpacity
to True.
For a version of this script that does animation, see
newcolor_10.ncl on the
RGB/A example page.
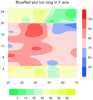
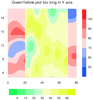
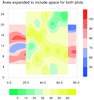 overlay_13.ncl
overlay_13.ncl:
This example shows what happens when you try to overlay two plots that
don't have the same X and Y axis ranges. The X/Y axis from the "base" plot
is the one that gets used for both plots, which may cause your "overlay"
plot to be cut off if its X and/or Y axis outside the range of the
X/Y axis of the "base" plot.
In this example, the X axis of the second plot is longer than the first, and
the Y axis of the first plot is longer than the second. The first image
shows what happen when you overlay plot #2 on plot #1. The second image
shows what happen when you overlay plot #1 on plot #2.
For the third image, the X/Y range was increased to be large enough to accommodate
both plots.
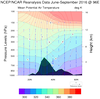 overlay_14.ncl
overlay_14.ncl:
This example illustrates overlaying an 'xy-object' onto a 'contour-object.'
The original source code was from:
- Ehimen Williams: Institute of Meteorology and Geophysics
- University of Cologne, Germany
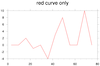
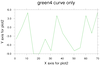
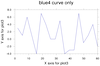
 overlay_15.ncl
overlay_15.ncl:
This example overlays two XY plots on a third XY plot (the base
plot). For illustrative purposes, the three individual plots are
drawn, and then the fourth image shows the overlaid plots.
This script shows how the overlay procedure
adopts the X/Y axis from the base plot. This means that the overlaid
plots may be cut off if their axis ranges are outside the axis ranges
of the base plot. The overlaid curves will be plotted correctly, but
you will note in the fourth image that the red and green curves are
truncated because they don't fit in the same range as the blue curve.
If you want the axes of the base plot to be large enough to encompass
all overlaid curves, then you will need to set the resources
trXMinF /
trXMaxF /
trYMinF /
trYMaxF.
Also note that the main title and the X and Y axis titles from the
base plot will be inherited from the base plot. This example uses
setvalues to change the titles after the
plot is created, but before overlay is called.
For an example that shows how to set the axis ranges and do more
customization of titles, see example overlay_16.ncl below.